Difference between revisions of "Category:Gospel of Luke (text)"
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
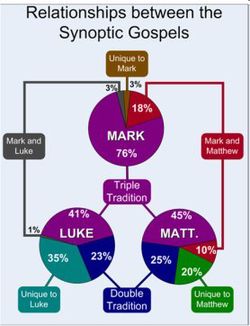
The '''Gospel of Luke ''' is a [[New Testament]] document. | [[File:Mark Matthew Luke.jpg|thumb|250px|The Synoptic Gospels]] | ||
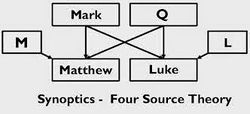
[[File:Q Mark Sources.jpg|thumb|250px|The Q Hypothesis]] | |||
*[[:Category:Texts|BACK TO THE TEXTS--INDEX]] | |||
The '''Gospel of Luke ''' (see [http://www.devotions.net/bible/42luke.htm Online Text]) is a [[New Testament]] document. | |||
* See [[Q Gospel]] / [[Gospel of Mark]] / [[Gospel of Matthew]] / [[Gospel of John]] / [[Gospel of Thomas]] | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
====Some notes on the relationship between Luke and the previuos gospels==== | |||
Mark was the Gospel of Peter. | |||
Matthew was in the line of [[James]], the brother of Jesus. | |||
Luke was a Jewish-Hellenistic Christian, largely following the teachings of Paul. | |||
---- | |||
Matthew - Jesus is the new, strong leader needed by the Jews after the catastrophe of 70 (he is the son of Abraham, the son of David, the new Moses, the new lawgiver…). See Jesus’ genealogy. | |||
Luke-Acts - Luke-Acts is profoundly influenced by Paul | |||
Jesus belongs to the entire humankind. He is the light of Gentiles (the new Adam, the Savior of humankind, etc.). See Jesus’ genealogy | |||
---- | |||
Matthew - Jesus’ story starts and ends in Galilee. Every time Jesus preached in Jerusalem, he was rejected. Jesus is the leader of an anti-Jerusalem movement. | |||
Luke-Acts – Jesus’ story start in the Temple. No Magi, no persecution by Herod, no stay in Egypt. On the contrary Jesus is presented to the Temple and preached in the Temple, even when he was a child. John the Baptist is not the only voice announcing the coming of the Messiah from within Judaism. The first Christian community was born in Jerusalem, at the heart of Judaism. Jesus is the personification of Judaism as a whole and the story of his movement testifies how the center of Judaism has moved from Jerusalem… Luke’s story ends in Rome, following Paul… as the center of Judaism has now moved from Jerusalem to the Diaspora (see Paul’s “parallel life”) | |||
---- | |||
Matthew – Jesus preached only to the “lost sheep” of the House of Israel. | |||
Luke-Acts – Jesus is constantly pushing his disciples to preach outside the boundaries of Israel | |||
---- | |||
Matthew - Jesus gave the new Torah from the mountain; see [[Sermon on the Mount]]. | |||
Luke-Acts – Jesus preached “in a flat land at the border with the Gentile land” | |||
---- | |||
Matthew-Mark – Two communal meals (on for the Jews, one for Gentiles) | |||
Luke-Acts – Only one communal meals for all disciples. | |||
---- | |||
Matthew – No special role for women | |||
Luke-Acts – Female disciples followed Jesus and supported the movement (8:1-2) | |||
---- | |||
Mark and Matthew – Pilate shares some responsibility for the killing of Jesus. | |||
Luke – Jesus was killed in spite of the opposition of Pilate and the Romans. Pilate and the Centurion proclaim Jesus’ innocence. | |||
---- | |||
Mark and Matthew – No special role for the Holy Spirit | |||
Luke-Acts – History is divided in three stages: the time of the Father (prophecy), the time of the Son (revelation), and the time of the Holy Spirit (mission). The Church is constituted and led by the Spirit. The end is not as imminent | |||
==Gospel of Luke in manuscript tradition== | ==Gospel of Luke in manuscript tradition== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 80: | ||
*[[Prologue of Luke]] (1:1-4) // no parallel; cf. Mark 1:1; Matthew 1:1; John 1:1-18 | *[[Prologue of Luke]] (1:1-4) // no parallel; cf. Mark 1:1; Matthew 1:1; John 1:1-18 | ||
*[[Annunciation to | *[[Annunciation to Zacharias]] (1:5-25) // no parallel | ||
*[[Annunciation to Mary]] (1:26-38) // no parallel | *[[Annunciation to Mary]] (1:26-38) // no parallel | ||
| Line 61: | Line 126: | ||
====Chapter 5==== | ====Chapter 5==== | ||
*[[Call of the First Disciples]] (5:1-11) // Mark 1:16-20; Matthew 4:18-22; cf. John 1:35-51 | *[[Call of the First Disciples]] & [[Miraculous Catch of Fish]] (5:1-11) // Mark 1:16-20; Matthew 4:18-22; cf. John 1:35-51 | ||
*[[Cleansing a Leper]] (5:12-16) // Mark 1:40-45; Matthew 8:1-4 | *[[Cleansing a Leper]] (5:12-16) // Mark 1:40-45; Matthew 8:1-4 | ||
| Line 233: | Line 298: | ||
*[[Unjust Steward]] (16:1-12) // no parallel | *[[Unjust Steward]] (16:1-12) // no parallel | ||
*[[God and Mammon]] ( | *[[God and Mammon]] (16:13) // Matthew 6:24 | ||
*[[Rich Man and Lazarus]] (16:19-31) // no parallel | *[[Rich Man and Lazarus]] (16:19-31) // no parallel | ||
| Line 258: | Line 323: | ||
====Chapter 19==== | ====Chapter 19==== | ||
*[[ | *[[Call of Zacchaeus]] (19:1-10) // no parallel | ||
*[[Talents]] (19:11-27) // Matthew 25:14-30 | *[[Talents]] (19:11-27) // Matthew 25:14-30 | ||
| Line 294: | Line 359: | ||
*[[Peter's Denial]] (I) (22:31-34) // Mark 14:27-31; Matthew 26:31-35; John 13:36-38 | *[[Peter's Denial]] (I) (22:31-34) // Mark 14:27-31; Matthew 26:31-35; John 13:36-38 | ||
*[[Arrest of Jesus]] (22:39-53) // Mark 14:32–52; Matthew 26:36-56; cf. John 18:3-12 | *[[Arrest of Jesus|Arrest of Jesus and Healing of a Servant's Ear]] (22:39-53) // Mark 14:32–52; Matthew 26:36-56; cf. John 18:3-12 | ||
*[[Trial of Jesus before the High Priest]] (I) (22:54) // Mark 14:53–65; Matthew 26:57-68; John 18:12-14 | *[[Trial of Jesus before the High Priest]] (I) (22:54) // Mark 14:53–65; Matthew 26:57-68; John 18:12-14 | ||
| Line 328: | Line 393: | ||
*[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gospel_of_Luke Wikipedia] | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gospel_of_Luke Wikipedia] | ||
*[http://www.earlychristianwritings.com/luke.html Early Christian Writings] | *[http://www.earlychristianwritings.com/luke.html Early Christian Writings] | ||
[[Category:Texts | |||
[[Category:Index (database)]] | |||
[[Category:Texts (database)]] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:16, 1 January 2021
The Gospel of Luke (see Online Text) is a New Testament document.
Overview
Some notes on the relationship between Luke and the previuos gospels
Mark was the Gospel of Peter.
Matthew was in the line of James, the brother of Jesus.
Luke was a Jewish-Hellenistic Christian, largely following the teachings of Paul.
Matthew - Jesus is the new, strong leader needed by the Jews after the catastrophe of 70 (he is the son of Abraham, the son of David, the new Moses, the new lawgiver…). See Jesus’ genealogy.
Luke-Acts - Luke-Acts is profoundly influenced by Paul Jesus belongs to the entire humankind. He is the light of Gentiles (the new Adam, the Savior of humankind, etc.). See Jesus’ genealogy
Matthew - Jesus’ story starts and ends in Galilee. Every time Jesus preached in Jerusalem, he was rejected. Jesus is the leader of an anti-Jerusalem movement.
Luke-Acts – Jesus’ story start in the Temple. No Magi, no persecution by Herod, no stay in Egypt. On the contrary Jesus is presented to the Temple and preached in the Temple, even when he was a child. John the Baptist is not the only voice announcing the coming of the Messiah from within Judaism. The first Christian community was born in Jerusalem, at the heart of Judaism. Jesus is the personification of Judaism as a whole and the story of his movement testifies how the center of Judaism has moved from Jerusalem… Luke’s story ends in Rome, following Paul… as the center of Judaism has now moved from Jerusalem to the Diaspora (see Paul’s “parallel life”)
Matthew – Jesus preached only to the “lost sheep” of the House of Israel.
Luke-Acts – Jesus is constantly pushing his disciples to preach outside the boundaries of Israel
Matthew - Jesus gave the new Torah from the mountain; see Sermon on the Mount.
Luke-Acts – Jesus preached “in a flat land at the border with the Gentile land”
Matthew-Mark – Two communal meals (on for the Jews, one for Gentiles)
Luke-Acts – Only one communal meals for all disciples.
Matthew – No special role for women
Luke-Acts – Female disciples followed Jesus and supported the movement (8:1-2)
Mark and Matthew – Pilate shares some responsibility for the killing of Jesus.
Luke – Jesus was killed in spite of the opposition of Pilate and the Romans. Pilate and the Centurion proclaim Jesus’ innocence.
Mark and Matthew – No special role for the Holy Spirit
Luke-Acts – History is divided in three stages: the time of the Father (prophecy), the time of the Son (revelation), and the time of the Holy Spirit (mission). The Church is constituted and led by the Spirit. The end is not as imminent
Gospel of Luke in manuscript tradition
Gospel of Luke in Scholarship
Gospel of Luke in Fiction
Synopsis
Chapter 1
- Prologue of Luke (1:1-4) // no parallel; cf. Mark 1:1; Matthew 1:1; John 1:1-18
- Annunciation to Zacharias (1:5-25) // no parallel
- Annunciation to Mary (1:26-38) // no parallel
- Visitation of Mary (1:39-56) // no parallel
- Birth of John the Baptist (1:57-80) // no parallel
Chapter 2
- Birth of Jesus (2:1-7) // no parallel
- Adoration of the Shepherds (2:8-20) // no parallel
- Circumcision of Jesus (2:21) // no parallel
- Presentation of Jesus at the Temple (2:22-38) // no parallel
- Infancy of Jesus (2:39-40) // no parallel
- Jesus among the Doctors (2:41-50) // no parallel
- Childhood of Jesus (2:51-52) // no parallel
Chapter 3
- Preaching of John the Baptist (3:3-18) // Mark 1:1-8; Mt 3:1-12; cf. Jn 1:6-8.15.19-36
- Baptism of Jesus (3:21-22) // Mark 1:9-11; Matthew 3:13-17; cf. Jn 1:29-34
- Genealogy of Jesus (3:23-38) // Matthew 1:1-17
Chapter 4
- Temptation of Jesus (4:1-13) // Mark 1:12-13; Matthew 4:1-11
- Beginning of Galilean Ministry (4:14-15) // Mark 1:14-15; Matthew 4:12-17; cf. John 4:1-3
- Hometown Rejection (4:16-30) // Mark 6:1–6a; Matthew 13:53-58
- Man with an Unclean Spirit (4:31-37) // Mark 1:21-28
- Peter's Mother-in-Law (4:38-41) // Mark 1:29-34; Matthew 8:14-17
- Preaching Tour (4:42-44) // Mark 1:32-39
Chapter 5
- Call of the First Disciples & Miraculous Catch of Fish (5:1-11) // Mark 1:16-20; Matthew 4:18-22; cf. John 1:35-51
- Cleansing a Leper (5:12-16) // Mark 1:40-45; Matthew 8:1-4
- Paralytic at Capernaum (5:17-26) // Mark 2:1-12; Matthew 9:1-8
- Recruiting the Tax Collector (5:27-32) // Mark 2:13–17; Matthew 9:9-13
- Question about Fasting (5:33-39) // Mark 2:18–22; Matthew 9:14-17
Chapter 6
- Lord of the Sabbath (6:1-5) // Mark 2:23-28; Matthew 12:1-8
- Man with a Withered Hand (6:6-11) // Mark 3:1-6; Matthew 12:9-14
- Choosing of the Twelve (6:12-16) // Mark 3:13–19; Matthew 10:1-4
- Ministering to a Great Multitude (6:17-19) // Matthew 4:23-25
- Beatitudes (6:20-26) // Matthew 5:3-12
- Love for Enemies (6:27-36) // Matthew 5:38-48
- Judging Others (6:37-42) // Matthew 7:1-5; cf. Romans 2:1-5.
- Tree Known by Its Fruit (6:43-45) // Matthew 7:15-20
- Two Foundations (6:46-49) // Matthew 7:21-29
Chapter 7
- Centurion's Servant (7:1-10) // Matthew 8:5-13; cf. John 4:46-54
- Young Man from Nain (7:11-17) // no parallel
- Messengers from John the Baptist (7:18-35) // Matthew 11:2-19
- Anointing of Jesus (7:36-50) // Cf. Mark; Matthew; John
Chapter 8
- Women Disciples of Jesus (8:1-3) no parallel
- Sower (I) (8:4-8) // Mark 4:1–9); Matthew 13:1-9; Thomas 9; 1 Clement 24:5
- Purpose of the Parables (I) (8:9-10) // Mark 4:10-12; Matthew 13:10-17
- Sower (II) (8:11-15) // Mark 4:13-20; Matthew 13:18-23
- Lamp under a Bushel (8:16-18) // Mark 4:21–25
- Jesus' True Relatives (8:19-21) // Mark 3:31-35; Matthew 12:46-50
- Calming the Storm (8:22-25) // Mark 4:35–41; Matthew 8:23-27
- Gerasene Demoniac (8:26-39) // Mark 5:1–20; Matthew 8:28-34
- Raising of Jairus' Daughter (I) (8:40–42) // Mark 5:21–24; Matthew 9:18–19
- Bleeding Woman (8:43-48) // Mark 5:24-34; Matthew 9:20-22
- Raising of Jairus' Daughter (II) (8:49-56) // Mark 5:35–43; Matthew 9:23-26
Chapter 9
- Mission of the Twelve (9:1-6) // Mark 6:6b-13; Matthew 10:5-15
- Beheading of John the Baptist (9:7-9) // Mark 6:14-29; Matthew 14:1-12
- Feeding the 5000 (9:10-17) // Mark 6:30–44; Matthew 14:13-21; John 6:1-14
- Peter's Confession (9:18-21) // Mark 8:27–30; Matthew 16:13-20
- First Prediction of the Passion (9:22-27) // Mark 8:31-9:1; Matthew 16:21-28
- Transfiguration of Jesus (9:28-36) // Mark 9:2–13; Matthew 17:1-13
- Possessed Boy (9:37-43a) // Mark 9:14-29; Matthew 17:14-20
- Second Prediction of the Passion (9:43b-45) // Mark 9:30-32; Matthew 17:22-23
- Greatest in the Kingdom (9:46-48) // Mark 9:33-37; Matthew 18:1-5
- He Who Is Not against Us is for Us (9:49-50) // Mark 9:38–41
- Rejection in Samaria (9:51-56) no parallel
- Would-be Followers of Jesus (9:57-62) // Matthew 8:18-22
Chapter 10
- Seventy Disciples (I) (10:1-12) no parallel
- Woe to Unrepentant Cities (10:13-15) // Matthew 11:20-24
- Seventy Disciples (II) (10:17-20) no parallel
- Come to Me and Rest (10:21-22) // Matthew 11:25-30
- (10:23-24)
- Great Commandment (10:25-28) // Mark 12:28–34; Matthew 22:34-40
- Good Samaritan (10:29-37) no parallel
- Jesus at the Home of Martha and Mary (10:38-42) no parallel
Chapter 11
- Lord's Prayer (11:2-4) // Matthew 6:9-13
- Friend at Night (11:5-8) no parallel
- Ask, Seek, Knock (11:9-13) // Matthew 7:7-12
- Jesus and Beelzebul (11:14-23) // Mark 3:22–30; Matthew 12:22-32
- Return of the Unclean Spirit (11:24-26) // Matthew 12:43-45
- (11:27-28) no parallel
- Demand for a Sign (11:29-32) // Mark 8:11–13; Matthew 12:38-42
- Light of the Body (11:33-36) // Matthew 6:22-23
- (11:37-53)
Chapter 12
- Warning against Hypocrisy (12:1-3) no parallel
- Whom to Fear (12:2-7) // Matthew 10:26-31
- Confessing Christ (12:8-12) // Matthew 10:32-33
- Rich Fool (12:13-21) // Thomas 63
- Birds of Heaven (12:22-34) // Matthew 6:25-34
- Unfaithful Servant (12:34-48) // Matthew 24:45-51
Chapter 13
- Repent or Perish (13:1-5) no parallel
- Barren Fig Tree (13:6-9) no parallel
- Crippled Woman (13:10-17) no parallel
- Mustard Seed (13:18-19) // Mark 4:30–32; Matthew 13:31-32; Thomas 20
- Narrow Gate (13:22-30) // Matthew
- Lament over Jerusalem (13:31-35) // Matthew 23:37-39
Chapter 14
- Man with Dropsy (14:1-6) no parallel
- Marriage Feast (14:15-24) // Matthew 22:1-14
- Teaching about Relatives (14:25-36) // Matthew ; Thomas
- Counting the Cost (14:27-33) no parallel
- Salt and Light (14:34-35) // Mark 9:50; Matthew 5:13-16
Chapter 15
- Lost Sheep (15:1-7) // Matthew 18:10-14; Thomas 107; Gospel of Truth 31-32; cf. John 10:1-18
- Lost Coin (15:8-9) // no parallel
- Prodigal Son (15:11-32) // no parallel
Chapter 16
- Unjust Steward (16:1-12) // no parallel
- God and Mammon (16:13) // Matthew 6:24
- Rich Man and Lazarus (16:19-31) // no parallel
Chapter 17
- Master and Servant (17:7-10) no parallel
- Cleansing Ten Lepers (17:11-19) no parallel
Chapter 18
- Unjust Judge (18:1-9) // no parallel
- Pharisee and the Publican (18:10-14) // no parallel
- Little Children Blessed (18:15-17) // Mark 10:13-16; Matthew 19:13-15
- Rich Young Man (18:18-30) // Mark 10:17–31; Matthew 19:16-30
- Third Prediction of the Passion (18:31-34) // Mark 10:32-34; Matthew 20:17-19
- Blind Bartimaeus (18:35-43) // Mark 10:46–52; Matthew 20:29-34
Chapter 19
- Call of Zacchaeus (19:1-10) // no parallel
- Talents (19:11-27) // Matthew 25:14-30
- Triumphal Entry into Jerusalem (19:28-40) // Mark 11:1–11; Matthew 21:1-11; John 12:12-19
- Lament over Jerusalem (19:41-44)
- Cleansing of the Temple (19:45-48) // Mark 11:15–19; Matthew 21:12-17; John 2:13-22
Chapter 20
- Question about Authority (20:1-8) // Mark 11:27-33; Matthew 21:23-27
- Wicked Husbandmen (20:9-19) // Mark 12:1–12; Matthew 21:33-46; Thomas 65-66
- Tribute to Caesar (20:20-26) // Mark 12:13–17; Matthew 22:15-22
- Question about the Resurrection (20:27-40) // Mark 12:18-27; Matthew 22:23-33
- Question about the Son of David (20:41-44) // Mark 12:35-37; Matthew 22:41-46
- Woe to the Scribes (20:45-47) // cf. Mark 12:38-40; Matthew 23:1-36
Chapter 21
- Coming Persecutions (21:12-17) // Mark 13:9-13; Matthew 10:16-25
Chapter 22
- Plot to Kill Jesus (22:1-2) // Mark 14:1-2; Matthew 26:1-5; John 11:45-53
- Betrayal of Judas (22:3-6) // Mark 14:10-11; Matthew 26:14-16
- Last Supper (22:7-23) // Mark 14:12–26; Matthew 26:17-30; John 13:21-30; 1 Corinthians 11:23-25
- Peter's Denial (I) (22:31-34) // Mark 14:27-31; Matthew 26:31-35; John 13:36-38
- Arrest of Jesus and Healing of a Servant's Ear (22:39-53) // Mark 14:32–52; Matthew 26:36-56; cf. John 18:3-12
- Trial of Jesus before the High Priest (I) (22:54) // Mark 14:53–65; Matthew 26:57-68; John 18:12-14
- Peter's Denial (II) (22:56-62) // Mark 14:66-72; Matthew 26:69-75; John 18:15-18.25-27
- Trial of Jesus before the High Priest (II) (22:63-71) // Mark 14:53–65; Matthew 26:57-68; John 18:15-18
Chapter 23
- Trial of Jesus before Pilate (I) (23:1-5) // Mark (15:1–20a), Matthew, John
- Trial of Jesus before Herod Antipas (23:6-12) // no parallel
- Trial of Jesus before Pilate (II) (23:13-25) // Mark (15:1–20a), Matthew, John
- Crucifixion of Jesus (23:26-49) // Mark (15:20b–41); Matthew; Luke; John
- Burial of Jesus (23:50-56) // Mark 15:42–47; Matthew 27:57-61; John 19:38-42
Chapter 24
- Empty Tomb (24:1-12) // Mark 16:1-8; Matthew 28:1-8; John 20:1-10
- Appearances of Jesus (24:13–49) // 1 Corinthians 15:3–9; Matthew 28:8–20; Mark 16:9-18; Acts 1:1–11; John 20:11–21:25
- Ascension of Jesus (24:50-53) // Acts 1:9-11; Mark 16:19-20
Related categories
- Jesus of Nazareth
- New Testament / Gospel of Mark / Gospel of Matthew / Gospel of John / Gospel of Thomas
External links
Pages in category "Gospel of Luke (text)"
The following 75 pages are in this category, out of 75 total.
1
- Commentarii initiatorii in qvatvor Evangelia (1521 Lefèvre), book
- The Gospel according to St. Luke (1880 Farrar), book
- Commentary on the Gospel of Luke (1884 Bliss), book
- The Gospel according to St. Luke (Greek Text) (1884 Farrar), book
- The Gospel according to St. Luke (1887 Lindsay), book
- Josephus und Lucas (1893 Krenkel), book
- Commentarius in Evangelium secundum S. Lucam (1896 Knabenbauer), book
- A Critical and Exegetical Commentary on the Gospel according to S. Luke (1896 Plummer), book
- Il Santo Vangelo di N.S. Gesù Cristo e gli Atti degli Apostoli (1904 Clementi, Genocchi, Semeria), book
- The Gospel according to St Luke (1911 Garvie), book
- Das Evangelium des Lucas (1913 Zahn), book
- St. Luke (1922 Ragg), book
- The Parable of Dives and Lazarus, and Enoch 22 (1922 Standen), essay
- Notes on St. Luke and the Acts (1928 Pallis), book
- The Gospel of Luke (1930 Manson), book
- The Gospel according to St. Luke (Greek Text) (1933 Luce), book
- Commentary on the Gospel of Luke (1950 Geldenhuys), book
- Luukkaan evankeliumi (1951 Nikolainen), book
- The Gospel of Luke (1964 Reicke), book
- The Gospel according to Luke (1965 Tinsley), book
- St Luke's Gospel and the Last Chapters of 1 Enoch (1966 Aalen), essay
- The Prelude to the Lukan Passion Narrative (1968 Vööbus), book
- Der Markus-Stoff bei Lukas (1971 Schramm), book
- The Passion Narrative of St. Luke (1972 Taylor, Owen), book
- The Gentiles and the Gentile Mission in Luke-Acts (1973 Wilson), book
- The Gospel according to St. Luke (1974 Morris), book
- Secundum Lucam (1975 Najera), oratorio
- Luca (1977 Ghidelli), book
- Études sur l'oeuvre de Luc (1978 Georges), book
- The Gospel of Luke ~ NIGTC (1978 Marshall), book
- The Gospel according to Luke I-IX (1981 Fitzmyer), book
- Reading Luke (1982 Talbert), book
- Luke and the Law (1983 Wilson), book
- Good News to the Poor: Wealth and Poverty in Luke-Acts (1984 Pilgrim), book
- The Gospel according to Luke X-XXIV (1985 Fitzmyer), book
- El evangelio según Lucas (1986-2005 Fitzmyer / Mínguez), book (Spanish ed.)
- Community and Gospel in Luke-Acts (1987 Esler), book
- The Jews in Luke-Acts (1987 Sanders), book
- The Demise of the Devil: Magic and the Demonic in Luke's Writings (1989 Garrett), book
- Luke (1989-93 Nolland), book
- What Are They Saying about Luke? (1989 Powell), book
- Luke (1990 Craddock), book
- 擘開生命之餅 : 路加五個獨有的比喻 (Perspective on Life: Five Lucan Parables / 1990 Fung), book
- Neither Here nor There: Luke 17:20-21 and Related Sayings in Thomas, Mark and Q (1990 Uro), book
- Citazioni patristiche e critica testuale neotestamentaria: il caso di Lc 12,49 (1990 Visonà), book
- Conflict in Luke: Jesus, Authorities, Disciples (1991 Kingsbury), book
- Luke-Acts: Scandinavian Perspectives (1991 Luomanen), edited volume
- Conflicto en Lucas: Jesús, autoridades, discípulos = Conflict in Luke: Jesus, Authorities, Disciples (1992 Kingsbury / Godoy), book (Spanish ed.)
- Images of Judaism in Luke-Acts (1992 Tyson), book
- The Preface to Luke's Gospel (1993 Alexander), book
- The Plan of God in Luke-Acts (1993 Squires), book
- Pseudo-Philo und Lukas (1994 Reinmuth), book
- El Evangelio según san Lucas (1995-2010 Bovon / Ortiz/Piñero), book (Spanish ed.)
- Luke (1995 Ringe), book
- Establishment Violence in Philo and Luke (1995 Seland), book
- L'Évangile de l'enfance (Luc 1-2) selon le proto-Luc (1997 Boismard), book
- The Gospel of Luke (1997 Green), book
- Luke's Gospel (1998 Knight), book
2
- Historia de la tradición sinóptica (2000 Bultmann / Ruiz-Garrido), book (Spanish ed.)
- Comment Luc a remanié l'évangile de Jean (2001 Boismard), book
- Recht, Gerechtigkeit und Religion im Lukasevangelium (2001 Bormann), book
- Reading Issues of Wealth and Poverty in Luke-Acts (2001 Phillips), book
- A Feminist Companion to Luke (2002 Levine, Blickenstaff), edited volume
- The Trial of the Gospel: An Apologetic Reading of Luke's Trial Narratives (2002 Neagoe), book
- The Significance of Theophilus as Luke's Reader (2004 Garrison), book
- The Exorcism Stories in Luke-Acts (2004 Klutz), book
- The Interpretation of the Gospel of Luke (2005 Kealy), book
- 路加的耶穌故事 = Conflict in Luke: Jesus, Authorities, Disciples (2008 Kingsbury / Ou), book (Chinese ed.)
- Surprised by God: Praise Responses in the Narrative of Luke-Acts (2009 De Long), book
- The Assumed Authorial Unity of Luke and Acts (2009 Walters), book
- Scriptural Interpretation and Community Self-Definition in Luke-Acts and the Writings of Justin Martyr (2011 Wendel), book
- Salty Wives, Spirited Mothers, and Savvy Widows: Capable Women of Purpose and Persistence in Luke's Gospel (2012 Spencer), book
- Rejected Prophets: Jesus and His Witnesses in Luke-Acts (2013 McWhirter), book
- Torah Praxis after 70 CE: Reading Matthew and Luke-Acts as Jewish Texts (2013 Oliver), book
- For Theirs Is the Kingdom: Inclusion and Participation of Children in the Gospel according to Luke (2019 Lindeman Allen), book
Media in category "Gospel of Luke (text)"
The following 9 files are in this category, out of 9 total.
- 1987 Lachs.jpg 400 × 602; 52 KB
- 2007 Lehtipuu.jpg 314 × 500; 15 KB
- 2012 Bovon.jpg 446 × 500; 17 KB
- 2015 Batty (film) 2.jpg 707 × 1,000; 97 KB
- 2021 Oliver.jpg 329 × 499; 29 KB
- 2021 Wilson.jpg 329 × 499; 35 KB
- 2023 Friedeman.jpg 400 × 622; 99 KB
- 2023 Smith (book).jpg 996 × 1,500; 105 KB
- 2023 Sterling.jpg 400 × 604; 253 KB