Difference between revisions of "Category:Holocaust Children Studies"
(→1950s) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
* See [http://www.museumoftolerance.com/education/teacher-resources/holocaust-resources/children-of-the-holocaust/ Museum of Tolerance] | * See [http://www.museumoftolerance.com/education/teacher-resources/holocaust-resources/children-of-the-holocaust/ Museum of Tolerance] | ||
* See [ | * See [[Holocaust Children]] | ||
When World War II began in September 1939, there were approximately 1.6 million Jewish children living in the territories that the German armies or their allies would occupy. When the war in Europe ended in May 1945, more than 1.2 million and perhaps as many as 1.5 million Jewish children were dead, targeted victims in the Nazis’ calculated program of genocide. As Warsaw ghetto historian Emanuel Ringelblum wrote in 1942, “Even in the most barbaric times, a human spark glowed in the rudest heart, and children were spared. But the Hitlerian beast is quite different. It would devour the dearest of us, those who arouse the greatest compassion—our innocent children.” | When World War II began in September 1939, there were approximately 1.6 million Jewish children living in the territories that the German armies or their allies would occupy. When the war in Europe ended in May 1945, more than 1.2 million and perhaps as many as 1.5 million Jewish children were dead, targeted victims in the Nazis’ calculated program of genocide. As Warsaw ghetto historian Emanuel Ringelblum wrote in 1942, “Even in the most barbaric times, a human spark glowed in the rudest heart, and children were spared. But the Hitlerian beast is quite different. It would devour the dearest of us, those who arouse the greatest compassion—our innocent children.” | ||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
Many of the child survivors were now orphans or had been separated from their parents and relatives. Special DP camps were established for them in France, Italy (Selvino), Poland, Germany, the Netherlands... | Many of the child survivors were now orphans or had been separated from their parents and relatives. Special DP camps were established for them in France, Italy (Selvino), Poland, Germany, the Netherlands... | ||
== | == The Uniqueness of the Holocaust Experience == | ||
Why are we devoting so much time to children during the Holocaust? | |||
Children have rarely a life of their own. Their lives depend on the adults who take care of them. There are very little opportunities for children to be known apart from their families. The Jewish child is no exception (we know the names of only a few children who have distinguished themselves as children in Jewish history). | |||
In antiquity, most of the stories about children in the Bible present "ordinary" stories of child rivalry, family conflict, ecc. Only a few children are remembered for something really special that happened to them: Joseph (was sold as a slave, became the viceroy of Egypt), [[David]] (killed Goliath in battle), [[Daniel]] (served the Persian administration), etc. | |||
With the creation of schools more opportunities were offered to children to distinguished themselves outside of their own families, first of all for their learning as "exceptional students" (child prodigies). [[Josephus]], [[Jesus]], etc. The Rabbis had a term to עילוי or עלוי (i'lui) to denote child prodigies who distinguished themselves in the study of the Torah for their intelligence and memory. | |||
The Emancipation gave Jewish children (both boys and girls) the opportunity to distinguish themselves in other fields than religion, namely, as child singers, child actors, child musicians, as well as students of science. | |||
The normal situation of children is that adults are taking care of them. The Holocaust marked for an entire generation (around 1.6 millions of Jewish children in Europe) a complete reversal of their "normal" status. Adults became children (i.e. powerless), and children were forced to become adults. in order to survive, they had to take their lives in their own hands and make life-or-death decision for themselves and often also for their own relatives. This makes the Holocaust such a special time for the Jewish child, a time in which children have become protagonists without having asked for it. | |||
== Death and Survival == | |||
Around 90% of the 1.6 million Jewish children living in Europe under Nazi rule perished during the Holocaust: | |||
* At the beginning, after Hitler rose to power in 1933, Jewish children were not targeted for extermination. They suffered discrimination, exclusion and humiliation. They could no longer attend schools, they could not pursue an education, meet with non-Jewish friends, etc. Many tried to escape with or without their families especially after Kristallnacht (Nov 9-10, 1938), when Jewish synagogues and properties were destroyed in a massive pogrom. | |||
* After the beginning of the war, in September 1939, Jewish children experienced the ghettos. They began to die in the thousands because of hunger and disease. | |||
* Starting from June 1941, with the Nazi invasion of the Soviet Union, for the first time Jewish children in Eastern Europe were shoot with their families in mass executions. | |||
* In 1942 began the systematic killing of children, They were deported from the ghettos to the death camps. Only some children who lied about their age and could work, were able to survive. Others were able to flee before being captured. | |||
Only 10% of children survived the Holocaust (around 150.000): | |||
* (a) Refugees, with their families or alone ([[Kindertransport]]), who left continental Europe before the war started, or in some cases, even during the war. | |||
* (b) [[Hidden Children]] (with their families, with non-Jews, with the partisans, in Christian boarding schools, etc.) or on the run [[Street Children]] | |||
* (c) [[Nazi Ghettoes]] and [[Labor Camps]] (mostly adolescents, and a few younger children who were kept alive to serve as errand boys or for medical experiments). | |||
* (d) [[Family Camps]] (Bergen-Belsen, Theresienstadt) | |||
The rate of survival mostly depended on three factors: (1) Age; (2) Country; (3) Location. | |||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
Latest revision as of 11:09, 5 January 2023
Overview
- See [[1]]
When World War II began in September 1939, there were approximately 1.6 million Jewish children living in the territories that the German armies or their allies would occupy. When the war in Europe ended in May 1945, more than 1.2 million and perhaps as many as 1.5 million Jewish children were dead, targeted victims in the Nazis’ calculated program of genocide. As Warsaw ghetto historian Emanuel Ringelblum wrote in 1942, “Even in the most barbaric times, a human spark glowed in the rudest heart, and children were spared. But the Hitlerian beast is quite different. It would devour the dearest of us, those who arouse the greatest compassion—our innocent children.”
All Jews were targeted for death, but the mortality rate for children was especially high. Only around 150,000, or 6 to 11% of Europe’s prewar Jewish population of children survived as compared with 33% of the adults. The majority of them were teenagers, between 16 and 18 years old. The younger generally were not selected for forced labor, and the Nazis often carried out “children’s actions” to reduce the number of “useless eaters” in the ghettos. In the camps, children, the elderly, and pregnant women routinely were sent to the gas chambers immediately after arrival. The older had a better chance of survival.
Liberation from Nazi tyranny brought no end to the sufferings of the few Jewish children who survived the Holocaust. Many would face the future without parents, grandparents, or siblings. Even when they were half-orphans, frequently surviving parents did not have the means or desire to care for their children.
The largest group of surviving children (60,000) was in Romania. There were 15,000 children alive in France; 12,000 in Hungary as well as in Bulgaria; 7,000 in Poland as well as in Italy; 4,000 in Belgium as well as in the Netherlands; between 2,500 and 4,500 in Czechoslovakia; 2,400 in Greece. A few thousand children survived in Concentration camps: 1,600 in Theresienstadt, 900 at Buchenwald, 500 at Bergen-Belsen, 300 at Auschwitz, etc. As many as 60,000 child survivors emigrated to the United States after the war.
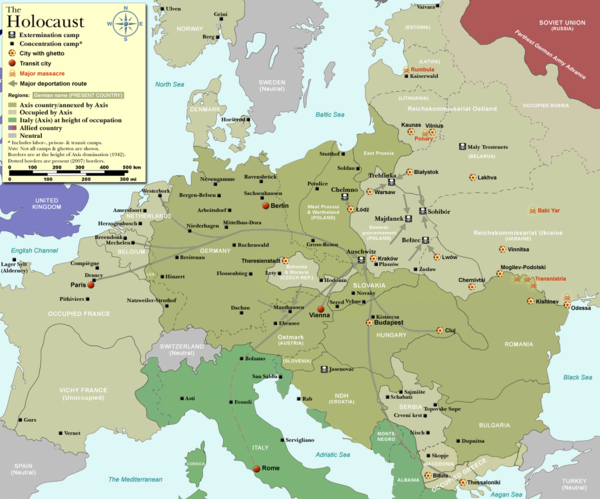
Geography and Chronology of the Holocaust
(1) Racial Laws, Discrimination, Segregation (1933-38)
The first to be affected by the Holocaust were the Jewish children living in Germany. They were subjected to racial laws, discriminated, expelled from schools. Many of them left emigrated with their families.
Second came in 1938 the Jewish children living in Austria and Jewish children living in Czechia. They were subjected to the same restrictive measures as their companions in Germany. Racial laws were enacted in Italy and Hungary as well.
(2) Persecution (1938-1939 & beyond)
- Refugees -- Kindertransport -- Kraus Rescue Mission -- One Thousand Children -- Tehran Children -- Fort Ontario
Kristallnacht marked the beginning of a new, more violent stage in the persecution. In Germany, Austria and Czechia, synagogues were burned, properties were destroyed. People were arrested, intimidated, some even murdered. Emigration now became a race against time. Nearby countries (and even much far away countries, like China) became places of refuge. It was difficult however to obtain visas since many countries had strict immigration laws. Many children left alone in a Kindertransport in order to reach safety abroad.
(3) Ghettos, Hunger, Disease, Forced Labor (1939-41 & beyond)
In Sept 1939 Germany conquered Eastern Poland. Children living in Poland were immediately subjected to violent persecution, and eventually forced to live in overcrowded ghetto where thousands of them died of hunger and disease.
In May 1940, the Holocaust also hit children living in the Netherlands, Belgium and France. In occupied Western countries, Nazi authorities initially refrained from open violence in order not to provoke reactions from the local population. Racial laws were enacted and Jews were gradually deprived of any right and freedom. In occupied France and Italy, then an ally of the Germans, children of "foreign Jews" (even those born in Italy) were forced to live in internment camps.
(4) Extermination (1941-1945)
- Mass Shootings -- Death Camps -- Concentration Camps -- Hidden Children -- Street Children -- Partisans
The Operation Barbarossa marked the beginning of the most violent stage in the Holocaust. For the first time, children living in Eastern Poland, Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia were directly targeted for extermination, first by specially appointed firing squads, then by deportation to death camps. By the beginning of 1942 death camps became fully operative. Jews were now deported from the Polish ghettos or from special transit camps in Western Europe directly to the gas chambers in Chelmno, Belzec, Treblinka, Sobibor, and Auschwitz. Children (especially orphans or the little ones) were the first ones to be murdered. (while only adolescents could have some chances as forced laborers).
After Sept 1943 the extermination was extended to Italy (now under German occupation) and following the German occupation of Hungary on 19 March 1944, also in Hungary.
(5) Liberation (1945)
Germany was losing the war. At the end of 1944-beginning 1945 the first concentration camps were liberated. Only a few children were found alive in Auschwitz on January 27, 1945. More consistent groups of children were liberated at Buchenwald, Berger-Belsen, Theresienstadt, Gunskirchen, ect. The end of the war also meant freedom for the thousands and thousands of children who were in hiding everywhere in Europe.
Many of the child survivors were now orphans or had been separated from their parents and relatives. Special DP camps were established for them in France, Italy (Selvino), Poland, Germany, the Netherlands...
The Uniqueness of the Holocaust Experience
Why are we devoting so much time to children during the Holocaust?
Children have rarely a life of their own. Their lives depend on the adults who take care of them. There are very little opportunities for children to be known apart from their families. The Jewish child is no exception (we know the names of only a few children who have distinguished themselves as children in Jewish history).
In antiquity, most of the stories about children in the Bible present "ordinary" stories of child rivalry, family conflict, ecc. Only a few children are remembered for something really special that happened to them: Joseph (was sold as a slave, became the viceroy of Egypt), David (killed Goliath in battle), Daniel (served the Persian administration), etc.
With the creation of schools more opportunities were offered to children to distinguished themselves outside of their own families, first of all for their learning as "exceptional students" (child prodigies). Josephus, Jesus, etc. The Rabbis had a term to עילוי or עלוי (i'lui) to denote child prodigies who distinguished themselves in the study of the Torah for their intelligence and memory.
The Emancipation gave Jewish children (both boys and girls) the opportunity to distinguish themselves in other fields than religion, namely, as child singers, child actors, child musicians, as well as students of science.
The normal situation of children is that adults are taking care of them. The Holocaust marked for an entire generation (around 1.6 millions of Jewish children in Europe) a complete reversal of their "normal" status. Adults became children (i.e. powerless), and children were forced to become adults. in order to survive, they had to take their lives in their own hands and make life-or-death decision for themselves and often also for their own relatives. This makes the Holocaust such a special time for the Jewish child, a time in which children have become protagonists without having asked for it.
Death and Survival
Around 90% of the 1.6 million Jewish children living in Europe under Nazi rule perished during the Holocaust:
- At the beginning, after Hitler rose to power in 1933, Jewish children were not targeted for extermination. They suffered discrimination, exclusion and humiliation. They could no longer attend schools, they could not pursue an education, meet with non-Jewish friends, etc. Many tried to escape with or without their families especially after Kristallnacht (Nov 9-10, 1938), when Jewish synagogues and properties were destroyed in a massive pogrom.
- After the beginning of the war, in September 1939, Jewish children experienced the ghettos. They began to die in the thousands because of hunger and disease.
- Starting from June 1941, with the Nazi invasion of the Soviet Union, for the first time Jewish children in Eastern Europe were shoot with their families in mass executions.
- In 1942 began the systematic killing of children, They were deported from the ghettos to the death camps. Only some children who lied about their age and could work, were able to survive. Others were able to flee before being captured.
Only 10% of children survived the Holocaust (around 150.000):
- (a) Refugees, with their families or alone (Kindertransport), who left continental Europe before the war started, or in some cases, even during the war.
- (b) Hidden Children (with their families, with non-Jews, with the partisans, in Christian boarding schools, etc.) or on the run Street Children
- (c) Nazi Ghettoes and Labor Camps (mostly adolescents, and a few younger children who were kept alive to serve as errand boys or for medical experiments).
- (d) Family Camps (Bergen-Belsen, Theresienstadt)
The rate of survival mostly depended on three factors: (1) Age; (2) Country; (3) Location.
External links
Subcategories
This category has the following 21 subcategories, out of 21 total.
- Holocaust Children Studies--1930s
- Holocaust Children Studies--1940s
- Holocaust Children Studies--1950s
- Holocaust Children Studies--1960s
- Holocaust Children Studies--1970s
- Holocaust Children Studies--1980s
- Holocaust Children Studies--1990s
- Holocaust Children Studies--2000s
- Holocaust Children Studies--2010s
- Holocaust Children Studies--2020s
*
Media in category "Holocaust Children Studies"
The following 72 files are in this category, out of 72 total.
- 1934 Bonham Carter.jpg 1,126 × 1,500; 149 KB
- 1945 Borwicz - Rost - Wulf.jpg 187 × 270; 10 KB
- 1946 Kaplan.jpg 187 × 269; 7 KB
- 1947 Grüss.jpg 188 × 268; 13 KB
- 1947 Hochberg - Grüss.jpg 128 × 184; 3 KB
- 1947 OSE.jpg 1,200 × 1,635; 355 KB
- 1947 Tenenbaum.jpg 650 × 907; 119 KB
- 1963 Lowrie.jpg 300 × 450; 23 KB
- 1979 Schwarberg.jpg 332 × 499; 32 KB
- 1982 Eisenberg.jpg 639 × 935; 131 KB
- 1984 Hemmendinger fr.jpg 345 × 499; 40 KB
- 1984 Klarsfeld.jpg 363 × 499; 32 KB
- 1984 Schwarberg en.jpg 300 × 434; 37 KB
- 1985 Klarsfeld en.jpg 185 × 260; 15 KB
- 1988 Eisen.jpg 333 × 499; 30 KB
- 1990 Lagnado.jpg 322 × 499; 38 KB
- 1991 Durlacher nl.jpg 120 × 200; 6 KB
- 1991 Dwork.jpg 339 × 499; 36 KB
- 1991 Gilbert.jpg 325 × 499; 31 KB
- 1993 Marks.jpg 322 × 499; 31 KB
- 1993 Valent.jpg 324 × 499; 30 KB
- 1994 Kestenberg.jpg 314 × 499; 18 KB
- 1994 Kraus.jpg 321 × 499; 21 KB
- 1994 Lukas.jpg 333 × 499; 40 KB
- 1994 Rosenberg.jpg 310 × 474; 31 KB
- 1994 Stein.jpg 296 × 474; 23 KB
- 1995 Boas.jpg 334 × 499; 30 KB
- 1996 Hochberg - Grüss en.jpg 326 × 499; 39 KB
- 1996 Kestenberg.jpg 429 × 640; 77 KB
- 1998 Durlacher en.jpg 292 × 499; 26 KB
- 1998 Kestenberg.jpg 314 × 499; 19 KB
- 1999 Fox.jpg 410 × 500; 36 KB
- 1999 Kustanowitz.jpg 371 × 499; 24 KB
- 2000 Harris doc.jpg 342 × 400; 17 KB
- 2000 Harris.jpg 400 × 605; 39 KB
- 2000 Hemmendinger Krell en.jpg 348 × 499; 33 KB
- 2001 Brostoff.jpg 333 × 499; 30 KB
- 2002 Zapruder.jpg 325 × 499; 20 KB
- 2004 Bailly.jpg 326 × 499; 28 KB
- 2004 Brenner de.jpg 325 × 499; 26 KB
- 2005 Nicholas.jpg 325 × 499; 33 KB
- 2006 Lee.jpg 400 × 604; 41 KB
- 2008 Vromen.jpg 333 × 499; 49 KB
- 2009 Abrams - Blaikie.jpg 375 × 499; 43 KB
- 2009 Bogner.jpg 337 × 499; 21 KB
- 2009 Brenner en.jpg 330 × 499; 29 KB
- 2010 Bailly English.jpg 332 × 499; 31 KB
- 2010 Tedesco.jpg 201 × 279; 16 KB
- 2011 Heberer.jpg 333 × 499; 32 KB
- 2012 Baumel-Schwartz.jpg 333 × 499; 33 KB
- 2012 Hodge.jpg 389 × 499; 36 KB
- 2013 Maida.jpg 316 × 499; 35 KB
- 2014 Eichengreen it.jpg 322 × 500; 39 KB
- 2014 Pressman.jpg 400 × 601; 26 KB
- 2016 Gigliotti Tempian.jpg 333 × 499; 33 KB
- 2016 Leytner.jpg 1,000 × 1,333; 115 KB
- 2016 Mazzeo.jpg 336 × 499; 43 KB
- 2016 Voigt.jpg 337 × 499; 26 KB
- 2017 Nelson.jpg 328 × 500; 31 KB
- 2018 Cohen.jpg 334 × 499; 27 KB
- 2018 Ouzan.jpg 333 × 499; 33 KB
- 2018 Strada - Spini.jpg 334 × 500; 43 KB
- 2019 Bell.jpg 388 × 499; 46 KB
- 2019 Dekel.jpg 331 × 499; 37 KB
- 2019 Kraus.jpg 318 × 499; 39 KB
- 2019 Serri.jpg 315 × 500; 27 KB
- 2019 Stańczyk.jpg 354 × 499; 28 KB
- 2020 Selmin.jpg 305 × 499; 37 KB
- 2021 Fontana.jpg 494 × 768; 94 KB
- 2021 Lang Korn Goldig.jpg 440 × 655; 32 KB
- 2021 Malaguti.jpg 355 × 500; 23 KB
- 2022 Sciapeconi.jpg 326 × 500; 22 KB