Difference between revisions of "United Monarchy"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:United Monarchy.png|thumb|250px]] | |||
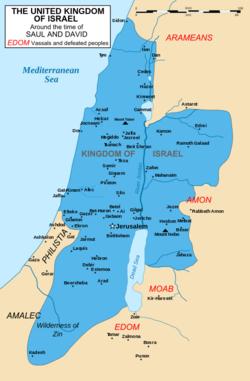
According to Jewish tradition, a '''United Monarchy''' existed in the land of Israel, following the period of the [[Judges]], from the establishment of the Kingdom of [[Saul]] (traditionally dated around 1047 BCE) to around 930 BCE, with the division of the [[Kingdoms of Judah and Israel]]. | According to Jewish tradition, a '''United Monarchy''' existed in the land of Israel, following the period of the [[Judges]], from the establishment of the Kingdom of [[Saul]] (traditionally dated around 1047 BCE) to around 930 BCE, with the division of the [[Kingdoms of Judah and Israel]]. | ||
Revision as of 07:02, 11 October 2020
According to Jewish tradition, a United Monarchy existed in the land of Israel, following the period of the Judges, from the establishment of the Kingdom of Saul (traditionally dated around 1047 BCE) to around 930 BCE, with the division of the Kingdoms of Judah and Israel.
< Kings : {Judges} -- United Monarchy (1047-930 BCE) -- Kingdoms of Judah and Israel (930-722 BCE) -- Neo-Assyrian Period (722-626 BCE) -- Kingdom of Josiah (626-609 BCE) -- Neo-Egyptian Period (609-605 BCE) -- Babylonian Period (605-539 BCE) -- {Second Temple Judaism}>
Overview
In contemporary scholarship the United Monarchy is generally held to be a literary construction and not a historical reality, pointing to the lack of archaeological evidence. It is generally accepted that a "House of David" existed, but David could have only been the king or chieftain of Judah, which was likely small. The northern kingdom was a separate development.