Difference between revisions of "Category:Jewish War (subject)"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| style="margin-top:10px; background:none;" | |||
| style="background:white; width:65%; border:1px solid #a7d7f9; vertical-align:top; color:#000; padding: 5px 10px 10px 8px; -moz-border-radius: 10px; -webkit-border-radius: 10px; border-radius:10px;" | | |||
<!-- ===================== COLONNA DI SINISTRA ==================== --> | |||
{| cellpadding="2" cellspacing="5" style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; background:transparent;" | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= [[Second Temple Studies]] -> (7) Jewish War | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo= Logo.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
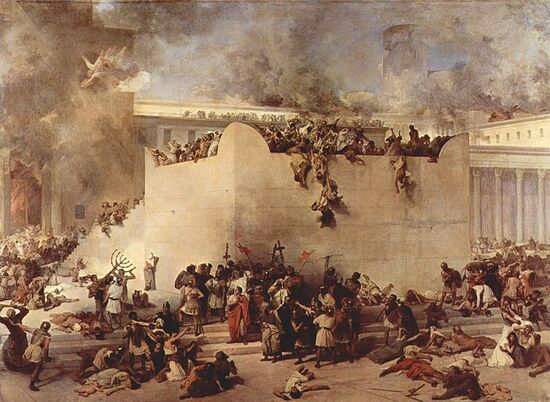
|content= [[File:Jerusalem Hayez.jpg|550px]] | |||
The [[Jewish War]] (66–73 CE), sometimes called The [[Great Revolt]], or the [[First Jewish-Roman War]] was the first of three major rebellions by the Jews of living in Judaea, against Rome. | The [[Jewish War]] (66–73 CE), sometimes called The [[Great Revolt]], or the [[First Jewish-Roman War]] was the first of three major rebellions by the Jews of living in Judaea, against Rome. | ||
< ''[[People]]'' : [[Josephus] -- [[John of Giscala]] -- [[Eleazar ben Simon]] -- [[Simon bar Giora]] -- [[Eleazar ben Yair]] -- [[Ananus ben Ananus]] -- [[Joshua ben Gamaliel]] -- [[Matthias ben Theophilus]] -- [[Phannias ben Samuel]] -/- [[Agrippa II]] -- [[Berenice]] -- [[Tiberius Alexander]] -/- [[Nero]] -- [[Gessius Florus]] -- [[Cestius Gallus]] -- [[Vespasian]] -- [[Titus]] -- [[Cerialis]] -- [[Lucilius Bassus]] -- [[Lucius Flavius Silva]] > | |||
< ''[[Events]]'' : [[Destruction of the Second Temple]] -- [[Fall of Masada]] > | |||
== | *This page is edited by [[Samuele Rocca]], Israel | ||
}} | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= Persian Period -- Overview | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo = logo.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= | |||
The [[Jewish]] War began in the year 66 CE, initially due to Greek and Jewish religious tensions. The Roman military garrison of [[Jerusalem]] was overrun by rebels, who later defeated the Roman army, under the leadership of [[Cestius Gallus]] the Roman governor of [[Syria]], at the [[Battle of Beth Horon]]. While the moderate leaders of the rebellion organized a government in [[Jerusalem]], the rebellion spread to the whole of [[Judaea]]. The emperor [[Nero]] handled the command of the Roman army to [[Vespasian]], who was assisted by various clients–kings, including the Jewish King [[Herod Agrippa II]]. In 67 CE, [[Vespasian]] moved against the Jewish stronghold in [[Galilee]], under the overall command of [[Josephus]] (Joseph ben Mattatihu). The Roman army overhelmed the Jewish forces in various sieges, as at [[Jotapata]] and [[Gamla]]. [[Josephus]] surrounded and later in the war would side with the Romans. By the end of the year [[Galilee]] was restored to [[Agrippa II]]. The next year, in 68 CE, [[Vespasian]] moved against [[Judaea]], and the neighboring regions. However the fall of [[Nero]] and the Year of the Four Emperors brought a stalemate in the war. Meanwhile in [[Jerusalem]], the moderate Jewish leadership was defeated and killed by the extremist [[Zealots]], under the leadership of [[John of Giscala]], [[Simon bar Giora]] and [[Eleazar ben Simon]]. In 70 CE, Titus, the son of [[Vespasian]] who was left behind by his father, now emperor, to continue the [[Jewish War]], besieged and conquered [[Jerusalem]]. The vast majority of the population was killed or enslaved, the city was burned, and the [[Temple]] razed down. The [[Jewish War]] ended only in 73 CE, with the conquest of the fortress of [[Masada]]. There a group of [[Sicarii]] hold on under the leadership of [[Eleazar ben Yair]]. The Roman commander, [[Flavius Silva]] succeeded in conquering the fortress. According to [[Josephus]] the [[Sicarii]] preferred to commit suicide together with their families, rather than be enslaved by the Romans. | The [[Jewish]] War began in the year 66 CE, initially due to Greek and Jewish religious tensions. The Roman military garrison of [[Jerusalem]] was overrun by rebels, who later defeated the Roman army, under the leadership of [[Cestius Gallus]] the Roman governor of [[Syria]], at the [[Battle of Beth Horon]]. While the moderate leaders of the rebellion organized a government in [[Jerusalem]], the rebellion spread to the whole of [[Judaea]]. The emperor [[Nero]] handled the command of the Roman army to [[Vespasian]], who was assisted by various clients–kings, including the Jewish King [[Herod Agrippa II]]. In 67 CE, [[Vespasian]] moved against the Jewish stronghold in [[Galilee]], under the overall command of [[Josephus]] (Joseph ben Mattatihu). The Roman army overhelmed the Jewish forces in various sieges, as at [[Jotapata]] and [[Gamla]]. [[Josephus]] surrounded and later in the war would side with the Romans. By the end of the year [[Galilee]] was restored to [[Agrippa II]]. The next year, in 68 CE, [[Vespasian]] moved against [[Judaea]], and the neighboring regions. However the fall of [[Nero]] and the Year of the Four Emperors brought a stalemate in the war. Meanwhile in [[Jerusalem]], the moderate Jewish leadership was defeated and killed by the extremist [[Zealots]], under the leadership of [[John of Giscala]], [[Simon bar Giora]] and [[Eleazar ben Simon]]. In 70 CE, Titus, the son of [[Vespasian]] who was left behind by his father, now emperor, to continue the [[Jewish War]], besieged and conquered [[Jerusalem]]. The vast majority of the population was killed or enslaved, the city was burned, and the [[Temple]] razed down. The [[Jewish War]] ended only in 73 CE, with the conquest of the fortress of [[Masada]]. There a group of [[Sicarii]] hold on under the leadership of [[Eleazar ben Yair]]. The Roman commander, [[Flavius Silva]] succeeded in conquering the fortress. According to [[Josephus]] the [[Sicarii]] preferred to commit suicide together with their families, rather than be enslaved by the Romans. | ||
| Line 51: | Line 70: | ||
By the end of 73 CE with the exception of most of the Gentile cities as [[Caesarea Maritima]], [[Sebaste]] as well as Greek cities, most notably [[Skythopolis]], Judaea was completely in ruin. The first step taken by the [[Flavians]] was to found colonies in Judaea to control the Jewish subjects. Already [[Nero]] had established the colony of [[Akko-Ptolemais]]. On its coins are depicted the standards of the [[Legion III Gallica]], [[Legion VI Ferrata]], [[Legion X Fretensis]], [[Legion XII Fulminata]]. Thus [[Vespasian]] established a colony at [[Caesarea Maritima]], the [[Colonia Prima Flavia Augusta Caesarea]]. Later on [[Domitian]] established another Roman colony at [[Flavia Neapolis]], modern Schechem. Flavian Judaea was a Senatorial Province, no more equestrian. This would probably stop the abuses that brought the Jews to revolt in 66 CE. Jerusalem was left in ruin, although the [[X Legio Fretensis]] remained there, encamped on the site of Herod's Palace, protected by the three towers of the citadel, which [[Titus]] spared from destruction. Jews, however, continued to live in the area around [[Jerusalem]]. [[Galilee]] was returned to the aging [[Agrippa II]], who died probably in 98 CE. With the death of [[Agrippa II]], the last Herodian ruler, [[Trajan]] annexed [[Galilee]] to the empire. Moreover in 106 CE, [[Trajan]] annexed the neighboring [[Nabatean kingdom]], as the [[Provincia Arabia]]. | By the end of 73 CE with the exception of most of the Gentile cities as [[Caesarea Maritima]], [[Sebaste]] as well as Greek cities, most notably [[Skythopolis]], Judaea was completely in ruin. The first step taken by the [[Flavians]] was to found colonies in Judaea to control the Jewish subjects. Already [[Nero]] had established the colony of [[Akko-Ptolemais]]. On its coins are depicted the standards of the [[Legion III Gallica]], [[Legion VI Ferrata]], [[Legion X Fretensis]], [[Legion XII Fulminata]]. Thus [[Vespasian]] established a colony at [[Caesarea Maritima]], the [[Colonia Prima Flavia Augusta Caesarea]]. Later on [[Domitian]] established another Roman colony at [[Flavia Neapolis]], modern Schechem. Flavian Judaea was a Senatorial Province, no more equestrian. This would probably stop the abuses that brought the Jews to revolt in 66 CE. Jerusalem was left in ruin, although the [[X Legio Fretensis]] remained there, encamped on the site of Herod's Palace, protected by the three towers of the citadel, which [[Titus]] spared from destruction. Jews, however, continued to live in the area around [[Jerusalem]]. [[Galilee]] was returned to the aging [[Agrippa II]], who died probably in 98 CE. With the death of [[Agrippa II]], the last Herodian ruler, [[Trajan]] annexed [[Galilee]] to the empire. Moreover in 106 CE, [[Trajan]] annexed the neighboring [[Nabatean kingdom]], as the [[Provincia Arabia]]. | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| Line 66: | Line 83: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== | ====External links==== | ||
*[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/First Jewish-Roman War Wikipedia] | |||
*[http://www.jewishencyclopedia.com/view.jsp?artid=64&letter=V Jewish Encyclopedia (1906)] | |||
*[ | |||
}} | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= Jewish War -- Highlights | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo = contents.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= | |||
}} | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= [[Jewish War (research)]] | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo = contents.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= | |||
}} | |||
|} | |||
|<!-- SPAZI TRA LE COLONNE --> style="border:5px solid transparent;" | | |||
<!-- ===================== COLONNA DI DESTRA ==================== --> | |||
| style="width:35%; border:1px solid #a7d7f9; background:#f5faff; vertical-align:top; padding: 5px 10px 10px 8px; -moz-border-radius: 10px; -webkit-border-radius: 10px; border-radius:10px;"| | |||
{| id="mp-right" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="5" style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; background:#f5faff; background:transparent;" | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= [[Jewish War (literature)]] | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo= contents.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= [[File:Literature.gif|300px]] | |||
}} | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= [[Jewish War (music)]] | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo= history.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= [[File:Music.jpg|300px]] | |||
}} | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= [[Jewish War (cinema)]] | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo= history.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= [[File:Cinema.jpg|300px]] | |||
}} | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= [[Jewish War (art)]] | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo= history.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= [[File:Art2.jpg|300px]] | |||
}} | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= [[Jewish War (fiction)]] | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo= history.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= | |||
}} | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
Revision as of 16:13, 16 January 2016
{{WindowMain
|
|
Pages in category "Jewish War (subject)"
The following 129 pages are in this category, out of 129 total.
1
- == == 1450s == == ==
- Josephus de la Bataille Judaique (Josephus's Jewish War / 1492), book
- De bello judaico (Jewish War / 1492 Palencia), book
- Guerra dei Giudei (1493), book
- == == 1500s == == ==
- The Triumph of Titus and Vespasian (1540 Romano), art
- The Destruction of Jerusalem (1577 Legge), play
- The Destruction of Jerusalem (1584 Smythe), play
- La gitana melancólica (1608 Aguilar), play
- Hierusalem Verwoest (Jerusalem Laid Desolate / 1620 Vondel), play (Dutch)
- The Jewes Tragedy (1626 Heminges), play
- Destruction of Jerusalem by Titus (1626 Poussin), art
- La Giudea distrutta da Vespasiano e Tito (1627 Finella), play
- L’ebrea famelica (The Famishing Jewess / 1640 Caputi / Vittori), oratorio (music & libretto)
- Los desagravios de Christo (1640 Cubillo de Aragón), play
- The Destruction of Jerusalem by Titus Vespasian (1677 Crowne), play
- Gerusalemme destrutta da Tito (1691 Cattani / Fineschi), oratorio
- Die Zerstörung Jerusalems (The Destruction of Jerusalem / 1692 Conradi / Postel), opera (music & libretto), Hamburg premiere
- La Gerusalemme convertita (1733 Caldara / Zeno), oratorio
- La Gerusalemme convertita (1733 Zeno), libretto
- La Gerusalemme convertita (1751 Galuppi / Zeno), oratorio
- Giovanni di Giscala (John of Giscala / 1754 Varano), play
- La Gerusalemme convertita (1755 Jommelli / Zeno), oratorio
- The Siege of Jerusalem by Titus Vespasian (1763 Latter), play
- The Siege of Jerusalem (1769 Bowes Strathmore), play
- Historia verdadera de la lamentable destrucción de Jerusalén, y triste desolación del pueblo Judaico (1777 Martín), book
- Gerusalemme distrutta (1812 Dusik), oratorio
- La distruzione di Gerusalemme (The Destruction of Jerusalem / 1812 Zingarelli / Sografi), opera (music & libretto), Milan premiere (cast)
- Jeruzsálem pusztulása (The Destruction of Jerusalem / 1814 Katona), play
- Solyme conquise; ou, La dispersion des juifs (1819 Desquiron), poetry
- The Wandering Jew (1820 Galt), novel
- The Fall of Jerusalem (1820 Milman), play
- The Wars of the Jews (1823 Johnstone / Brooke), juvenile novel & art
- Salathiel (1827 Croly), novel
- Geschichte der Römerherrschaft in Judäa und der Zerstörung Jerusalems (1847 @1847 Salvador / Eichler), book (German ed.)
- Histoire de la domination romaine en Judée et de la ruine de Jérusalem (1847 Salvador), book
- Siege and Destruction of Jerusalem by Titus (1850 Roberts), art
- Titus; oder, Die Zerstörung Jerusalems (1855 Kossarski), play
- Giovanni Giscala (John of Giscala / 1855 Rossi / Cavagnari), opera (music & libretto), Parma premiere
- L'ultimo giorno di Gerusalemme (1858 Lucchesi), opera
- La distruzione di Gerusalemme (The Destruction of Jerusalem / 1858 Pacini / Fioretti), oratorio (music & libretto), Florence premiere (cast)
- The Destruction of Jerusalem (1859 Ge), art
- The False Christ (1860 Charles), novel
- The Gladiators (1863 Whyte-Melville), novel
- Vespasian Hearing from One of His Generals of the Taking of Jerusalem by Titus (1866 Alma-Tadema), art
- Siége de Jotapata (1866 Parent), book
- Les derniers jours de Jérusalem (1866 Saulcy), book
- Salome (1867 Heywood), play
- Der Messias (1869 Gensichen), play
- The Triumph of Titus (1885 Alma-Tadema), art
- The Destruction of Jerusalem (1885 Landau), play
- Сказание о Флоре, Агриппе и Менахеме, сыне Иегуды (1886 Korolenko), novel
- For the Temple (1888 Henty), novel
- The Cross Triumphant (1895 Kingsley), novel
- Lucius Flavus (1898 Spillmann), novel (German)
- Josephus Flavius: Charakterystyka cztowieka i historyka na tle wspotczesnych wypadkow (1904 Balaban), book (Polish)
- Ahasver (1905 Diener/Hesslein), play
- Lucius Flavus (1906 Spillmann), novel (Italian ed.)
- The Forgotten Door (1907 Cowper), novel
- The City of Delight (1908 Miller), novel
- The Doomed City (1910 Carling), novel
- Metzadah (1927 Lamdan), poetry
- Be-lel zeh (1935 Bistritzky), play
- Yerushalayim ve-Romi: Yosifus Flavyus (1939 Bistritzky), play
- Bi-nefol Metsadah (1940 Braslavski), children's novel
- The Fall of Jerusalem and the Christian Church (1951 Brandon), book
- If I Forget Thee (1956 De Ropp), novel
- Aharit Metsadah (1959 Braslavski/Weil), children's novel
- Metsadah (1966 Yadin), book
- The Rider and His Horse (1968 Haugaard/Dillon), children's novel
- The Last Days (1968 Rayner), novel
- The Children of the Cave (1969 Livneh), children's novel
- The End of Days (1970 Gavron), novel
- Masada (1970 Greenberg), oratorio
- The Besieged (1972 Gant), novel
- Masada (1973 Berman), novel
- Masada Will Not Fall Again (1973 Greenspan), novel
- The Voices of Masada (1973 Kossoff), novel
- Metsadah 967 (Masada 967 / 1973 Tal / Eliraz), opera (music & libretto)
- A Time to Die (1974 Golden), novel
- Rzym i Jerozolima (1974 Krawczuk), book
- The Gladiator: Hill of the Dead (1975 Bulmer), novel
- Israel in Revolution, 6-74 CE (1976 Rhoads), book
- The Wolf of Masada (1978 Fredman), novel
- Last Night on Masada (1979 Douglas), novel
- Massada: les guerriers de Dieu (1979 Rachet), novel
- Zwölf Steine für Judäa (1979 Zitelmann), novel
- The Tenth Measure (1980 Segal), novel
- Masada (1980 Tacconi), novel
- Serpent (1981 Mosley), novel
- Ani zokher et Metsadah (1982 Ron-Feder/Harel), children's novel
- Sieg im Tod: Masada (1982 Weiss), novel
- Masada (1983 Brogan), novel
- Masada (1983 @1981 Sagal), TV mini-series (Italian ed.)
- `Ir melukah (1984 Baram), novel
- Lazare; ou, Le grand sommeil (1985 Absire), novel
- The Ruling Class of Judea: The Origins of the Jewish Revolt against Rome (1987 Goodman), book
- Masada (1987 Levy), oratorio
- The Tenth of Av (1988 Roseman), novel
- Le royaume de la Torah (1989 Baram), novel (French ed.)
- The Man of Masada (1990 Brogan), novel
- Flavius Josephus, the Zealots and Yavne (1994 Bohrmann), book (English ed.)
- The Road to Masada (1994 Elwood), novel
- Les voix de l'exil: un siècle à Jérusalem (1994 Lévy), novel
- The Fall of Jerusalem (1994 Wise), novel
- Milim (Metamorphosis of a Melody / 1996 Gitai), feature film
- Turbulent Times?: Josephus and Scholarship on Judaea in the First Century CE (1998 McLaren), book
- Masada: The Last Fortress (1998 Miklowitz), novel
- Le rivolte giudaiche (1999 Firpo), book
- Vespasian (1999 Levick), book
2
- Keeping Faith in the Dust (2000 Maltz), novel
- Return to Masada (2001 Makin), novel
- The First Jewish Revolt (2002 Berlin/Overman), edited volume
- אני, שלום בת שמואל (I, Shalom bat Shmuel / 2003 Ben-Guigui Yeger), novel
- The Fall of Jerusalem (2003 Muldowney / Fenton), oratorio
- The Masada Scroll (2006 Block/Vaughan), novel
- Ancient Rome: Rebellion (2006 Grieve), TV film
- Masada (2007 Siliato), novel
- Jerusalem's Traitor: Josephus, Masada, and the Fall of Judea (2008 Seward), non-fiction
- The Jews against Rome: War in Palestine AD 66-73 (2008 Sorek), book
- Masada: An Epic Story (2009 Eshel), book (English ed.)
- מצדה (Masada / 2009 Eshel), book
- == == 2010s == == ==
- Jewish Reactions to the Destruction of Jerusalem in AD 70 (2011 Jones), book
- The Jewish Revolt against Rome (2011 Popović), edited volume
- The Last Man (2012 Deutermann), novel
- The Last Temple (2012 Hanegraaff, Brouwer), novel
- Le guerre ebraiche dei Romani (The Jewish Wars of the Romans / 2015 Lewin), book
- The Destruction of Jerusalem in Early Modern English Literature (2015 Groves), book
Media in category "Jewish War (subject)"
The following 17 files are in this category, out of 17 total.
- 1637 * Poussin (art).jpg 800 × 593; 110 KB
- 1744 Bellotto (art).jpg 2,536 × 3,406; 740 KB
- 1840 * Peploe (novel).jpg 375 × 499; 25 KB
- 1846 * Kaulbach (art).jpg 723 × 600; 106 KB
- 1860 Lenbach (art).jpg 401 × 599; 78 KB
- 1867 * Hayez (art).jpg 800 × 585; 108 KB
- 1966 * Yadin.jpg 379 × 499; 48 KB
- 1970 * Gann (novel).jpg 300 × 436; 22 KB
- 1981 * Sagal (TV miniseries).jpg 214 × 317; 12 KB
- 1983 Pfanner - Hess - Schwanke.jpg 182 × 249; 3 KB
- 1991 Yarden.jpg 260 × 346; 11 KB
- 1993 * Rivers (novel).jpg 999 × 1,500; 133 KB
- 1995 * Ben-Yehuda.jpg 328 × 499; 26 KB
- 2007 * Goodman.jpg 324 × 499; 34 KB
- 2011 * Hoffman (novel).jpg 333 × 499; 29 KB
- 2020-E Chapot.jpg 400 × 601; 73 KB
- 2021 Giambrone.jpg 334 × 499; 13 KB