Difference between revisions of "Category:Babylonian Exile (subject)"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (25 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| style="margin-top:10px; background:none;" | |||
| style="background:white; width:65%; border:1px solid #a7d7f9; vertical-align:top; color:#000; padding: 5px 10px 10px 8px; -moz-border-radius: 10px; -webkit-border-radius: 10px; border-radius:10px;" | | |||
<!-- ===================== COLONNA DI SINISTRA ==================== --> | |||
{| cellpadding="2" cellspacing="5" style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; background:transparent;" | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= [[Second Temple Studies]] -> (1) Babylonian Exile | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo= Logo.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= [[File:Babylonian Exile Tissot.jpg|500px]] | |||
The '''Babylonian Exile''' goes from the conquest of Jerusalem by [[Nebuchadnezzar]] to the return and restoration of the Second Temple. | |||
< ''[[Second Temple Studies]]'' : ''[[Hebrew Bible Studies]]'' -- (1) [[Babylonian Exile]] -- (2) [[Persian Period]] -- (3) [[Greek Period]] -- (4) [[Maccabees|Maccabean Period]] -- (5) [[Roman Period]] -- see also [[Historical Jesus Studies]], and [[Christian Origins Studies]] > | |||
< ''People'' : [[Babylonian Kings]] -- [[Nebuchadnezzar]] -- [[Belshazzar]] -/- [[Davidic Kings]] -- [[Jehoiachin]] -/- [[Daniel]] -- [[Ezekiel]] -- [[Tobit]] -- [[Tobiah]] > | |||
== | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Babylonian_captivity Wikipedia] | ||
* This page is edited by [[Gabriele Boccaccini]], University of Michigan. | |||
}} | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= Sources | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo = contents.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= | |||
* See [[Book of Tobit]] -- [[Book of Daniel]] -- [[Book of Kings]] | |||
}} | |||
|} | |||
|<!-- SPAZI TRA LE COLONNE --> style="border:5px solid transparent;" | | |||
<!-- ===================== COLONNA DI DESTRA ==================== --> | |||
| style="width:35%; border:1px solid #a7d7f9; background:#f5faff; vertical-align:top; padding: 5px 10px 10px 8px; -moz-border-radius: 10px; -webkit-border-radius: 10px; border-radius:10px;"| | |||
{| id="mp-right" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="5" style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; background:#f5faff; background:transparent;" | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= [[Babylonian Exile (literature)|Literature]] | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo= contents.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= [[File:Literature.gif|180px]] | |||
}} | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= [[Babylonian Exile (music)|Music]] | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo= history.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= [[File:Music.jpg|180px]] | |||
}} | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= [[Babylonian Exile (cinema)|Cinema]] | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo= history.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= [[File:Cinema.jpg|180px]] | |||
}} | |||
{{WindowMain | |||
|title= [[Babylonian Exile (art)|Visual Arts]] | |||
|backgroundLogo= Bluebg_rounded_croped.png | |||
|logo= history.png | |||
|px= 38 | |||
|content= [[File:Art2.jpg|180px]] | |||
}} | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
== Overview == | |||
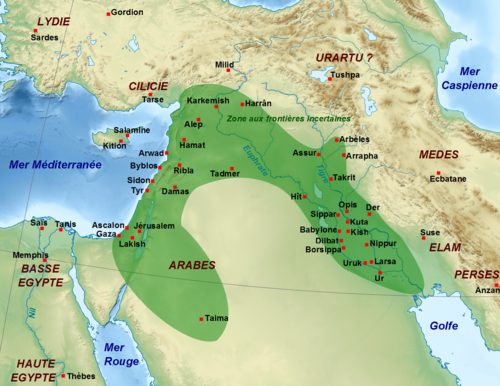
[[File:Babylonian Empire.png|600px]] | |||
'''605-562 BCE''' -- [[Nebuchadnezzar]], king of Babylon | |||
* '''605 BCE''' -- [[Nebuchadnezzar]], king of Babylon, defeated the Egyptians in the [[Battle of Charchemish]]. This meant the end of the Egyptian control of the region. Judah was now under Balylonian rule and [[Jehoiakim]] became a Babylonian vassal ("his servant for three years," 2 Kings 24:1) | |||
* '''601-597 BCE''' -- First attempt to rebel against the Babylonians. In the conflict between Egypt and Babylon, each claiming Canaan as their territory, King [[Jehoiakim]] sided with Egyptians, in spite of the warnings of Jeremiah (Jer 22:13-19). The Babylonians immediately invades Judah and besieged Jerusalem. [[Jehoiakim]] died before the town was taken (2 Kings 24:2-7). | |||
* '''597 BCE''' -- [[Jehoiakim]]'s son, [[Jehoiachin]] (also called Jeconiah), reigned only 3 months before Jerusalem fell (see the [[Annals of Nebuchadnezzar]]). | |||
* '''597 BCE''' -- Fall of Jerusalem and First Deportation. The Babyloninas took [[Jehoiachin]] captive to Babylon and exiled the entire royal court, nobles, priests (including [[Ezekiel]]) and skilled workers ("8,000/10,000 people," according to 2 Kings 24:14-16; "3,023 people," according to Jeremiah 52:28). | |||
* '''597-587 BCE''' -- Mattaniah, [[Jehoiachin]]'s uncle, was installed as the vassal king of Judah by the Babylonians, who changed his name to Zedekiah (see 2 Kings 24:18--25:21, and Jeremiah 52:1-27). [[Jehoiachin]], however, was spared (a table from the Babylonina royal archives gave him on 592 BCE the ambiguous title of "son of the king of Judah"). | |||
:The pro-Egyptian party in Palestine (led by the prophet Hananiah) continued to conspire for a rebellion against the Bablylonians. The exiles (led by the prophet-priest [[Ezekiel]]) remained loyal to king [[Jehoiachin]] and claimed that God had also left the temple and now was with his people in Babylon (see Ezekiel 1-24; esp. 8-11, dated 592 BCE). The nationalistic party of Jeremiah maintained that the Jews in Palestine and in Babylon had to accept God's punishment and couseled submission to the rule of Babylon (see Jeremiah 27-29). | |||
* '''587 BCE''' -- In a second attempt to rebel against the Bablylonians, Zedekiah renounced his fealty to [[Nebuchadnezzar]] and concluded a treaty with Egypt, despite the warnings of Jeremiah, who was arrested (Jer 34:37-38). [[Nebuchadnezzar]] marched into Judah, captured Jerusalem, demolished the walls of the town, and set the temple on fire (Jer 39:1-10). | |||
:According to 2 Kings (25:11-12), the Second Deportation affected "all the rest of population ... [except] some of the poorest of the land," or "832 people" according to Jeremiah (52:29). Zedekiah was imprisoned, blinded, and his sons were killed before him. A new vassal king was not appointed. Now in the Babylonian archives [[Jehoiachin]], although still in captivity, was recognized as the "king of Judah." The public role given to [[Jehoiachin]] by the Babylonians caused a split between the king (and his court) and the exile priest led by Ezekiel, who developed anti-monarchic attitudes (Ez 34). | |||
* '''587-582 BCE''' -- A Jewish scribe and a friend of Jeremiah, Gadaliah, was appointed by the Babylonians as the new governor of theose who remained in Judah (2 Kings 25:22-26). | |||
* '''582 BCE''' -- Gedaliah was assassinated by members of the pro-Egyptian party. The Babylonians immediately suffocated the revolt ("745 people" were deported, Jer 52:30). The remaining members of the pro-Egyptian party fled to Egypt to escape reprisal (Jer 40:7-41:18); they took the reluctant Jeremiah with them. For some time Judah was ruled by Babylonian governors. | |||
* '''562-560 BCE''' -- [[Evil-merodach]], king was of Babylon. | |||
*[ | * '''561 BCE''' -- [[Jehoiachin]] was released from prison and "a throne was given to him higher than that of the other kings who were with him in Babylon" (2 Kings 25:27-30; Jer 52:31-34). No longer captive, [[Jehoiachin]] was now the hostage king of Judah at the court of the king of Babylon and also the governo of Judah according to the centralized structure of the Babylonian administration. At the court of the king of Judah, scribed collected the ancient traditions of Israel in a continuous narrative from creation to king [[Jehoiachin]] (the bulk of the biblical books of Genesis thru 2 Kings), as well edited some prophetical books (such as the First Isaiah and Jeremiah). The theology was based on the prominent role of the [[House of David]] (2 Samuel 7:4-29) and on the monotheistic principles of the nationalistic movement. The exiled priests developed an alternative view of the future of Israel centered on a new Temple and a new priesthood led by the [[House of Zadok]] (Ezekiel 40-48). | ||
* '''560-556 BCE -- [[Neriglissar]], king of Babylon | |||
* '''556 BCE -- [[Labashi-Marduk]], king of Babylon | |||
[[ | * '''556-539 BCE -- [[Nabonidus]], king of Babylon | ||
Latest revision as of 19:39, 10 October 2020
|
< Second Temple Studies : Hebrew Bible Studies -- (1) Babylonian Exile -- (2) Persian Period -- (3) Greek Period -- (4) Maccabean Period -- (5) Roman Period -- see also Historical Jesus Studies, and Christian Origins Studies > < People : Babylonian Kings -- Nebuchadnezzar -- Belshazzar -/- Davidic Kings -- Jehoiachin -/- Daniel -- Ezekiel -- Tobit -- Tobiah >
Sources
|
|
Overview
605-562 BCE -- Nebuchadnezzar, king of Babylon
- 605 BCE -- Nebuchadnezzar, king of Babylon, defeated the Egyptians in the Battle of Charchemish. This meant the end of the Egyptian control of the region. Judah was now under Balylonian rule and Jehoiakim became a Babylonian vassal ("his servant for three years," 2 Kings 24:1)
- 601-597 BCE -- First attempt to rebel against the Babylonians. In the conflict between Egypt and Babylon, each claiming Canaan as their territory, King Jehoiakim sided with Egyptians, in spite of the warnings of Jeremiah (Jer 22:13-19). The Babylonians immediately invades Judah and besieged Jerusalem. Jehoiakim died before the town was taken (2 Kings 24:2-7).
- 597 BCE -- Jehoiakim's son, Jehoiachin (also called Jeconiah), reigned only 3 months before Jerusalem fell (see the Annals of Nebuchadnezzar).
- 597 BCE -- Fall of Jerusalem and First Deportation. The Babyloninas took Jehoiachin captive to Babylon and exiled the entire royal court, nobles, priests (including Ezekiel) and skilled workers ("8,000/10,000 people," according to 2 Kings 24:14-16; "3,023 people," according to Jeremiah 52:28).
- 597-587 BCE -- Mattaniah, Jehoiachin's uncle, was installed as the vassal king of Judah by the Babylonians, who changed his name to Zedekiah (see 2 Kings 24:18--25:21, and Jeremiah 52:1-27). Jehoiachin, however, was spared (a table from the Babylonina royal archives gave him on 592 BCE the ambiguous title of "son of the king of Judah").
- The pro-Egyptian party in Palestine (led by the prophet Hananiah) continued to conspire for a rebellion against the Bablylonians. The exiles (led by the prophet-priest Ezekiel) remained loyal to king Jehoiachin and claimed that God had also left the temple and now was with his people in Babylon (see Ezekiel 1-24; esp. 8-11, dated 592 BCE). The nationalistic party of Jeremiah maintained that the Jews in Palestine and in Babylon had to accept God's punishment and couseled submission to the rule of Babylon (see Jeremiah 27-29).
- 587 BCE -- In a second attempt to rebel against the Bablylonians, Zedekiah renounced his fealty to Nebuchadnezzar and concluded a treaty with Egypt, despite the warnings of Jeremiah, who was arrested (Jer 34:37-38). Nebuchadnezzar marched into Judah, captured Jerusalem, demolished the walls of the town, and set the temple on fire (Jer 39:1-10).
- According to 2 Kings (25:11-12), the Second Deportation affected "all the rest of population ... [except] some of the poorest of the land," or "832 people" according to Jeremiah (52:29). Zedekiah was imprisoned, blinded, and his sons were killed before him. A new vassal king was not appointed. Now in the Babylonian archives Jehoiachin, although still in captivity, was recognized as the "king of Judah." The public role given to Jehoiachin by the Babylonians caused a split between the king (and his court) and the exile priest led by Ezekiel, who developed anti-monarchic attitudes (Ez 34).
- 587-582 BCE -- A Jewish scribe and a friend of Jeremiah, Gadaliah, was appointed by the Babylonians as the new governor of theose who remained in Judah (2 Kings 25:22-26).
- 582 BCE -- Gedaliah was assassinated by members of the pro-Egyptian party. The Babylonians immediately suffocated the revolt ("745 people" were deported, Jer 52:30). The remaining members of the pro-Egyptian party fled to Egypt to escape reprisal (Jer 40:7-41:18); they took the reluctant Jeremiah with them. For some time Judah was ruled by Babylonian governors.
- 562-560 BCE -- Evil-merodach, king was of Babylon.
- 561 BCE -- Jehoiachin was released from prison and "a throne was given to him higher than that of the other kings who were with him in Babylon" (2 Kings 25:27-30; Jer 52:31-34). No longer captive, Jehoiachin was now the hostage king of Judah at the court of the king of Babylon and also the governo of Judah according to the centralized structure of the Babylonian administration. At the court of the king of Judah, scribed collected the ancient traditions of Israel in a continuous narrative from creation to king Jehoiachin (the bulk of the biblical books of Genesis thru 2 Kings), as well edited some prophetical books (such as the First Isaiah and Jeremiah). The theology was based on the prominent role of the House of David (2 Samuel 7:4-29) and on the monotheistic principles of the nationalistic movement. The exiled priests developed an alternative view of the future of Israel centered on a new Temple and a new priesthood led by the House of Zadok (Ezekiel 40-48).
- 560-556 BCE -- Neriglissar, king of Babylon
- 556 BCE -- Labashi-Marduk, king of Babylon
- 556-539 BCE -- Nabonidus, king of Babylon
Pages in category "Babylonian Exile (subject)"
The following 191 pages are in this category, out of 191 total.
1
- == == 1450s == == ==
- Tobias and the Angel (1460 Pollaiuolo), art
- Tobias and the Angel (1465 Gozzoli), art
- The Three Archangels and Tobias (1470 Botticini), art
- Raffaele e Tobiolo (Tobias and the Angel / 1475 Andrea della Robbia), art
- Storie sacre (Sacred Narratives / 1475c Tornabuoni), poetry
- Tobias and the Angel (1475 Verrocchio), art
- Tobias and the Angel (1480 Lippi), art
- Three Angels and Young Tobias (1485 Lippi), art
- Susanna and the Elders (1495 Pinturicchio), art
- == == 1500s == == ==
- Susanna and the Elders (1517 Lotto), art
- Healing of Tobit (1555 Hemessen), art
- Susanna and the Elders (1571 Bassano), art
- Susanna and the Elders (1610 Gentileschi), art
- Susanna and the Elders (1614 Lastman), art
- In sacros divinorvm Bibliorvm libros, Tobiam, Ivdith, Esther, Machabaeos, commentarius (1610 Serarius), book
- Daniel in the Lions' Den (1615 Rubens), art
- Susanna and the Elders (1617 Guercino), art
- Angel and Tobias with the Fish (1625 Lastman), art
- La cena del rey Baltasar (1634 Calderón de la Barca), play
- Belshazzar's Feast (1635 Rembrandt), art
- Susanna and the Elders (1647 Rembrandt), art
- Susanna and the Elders (1649 Koninck), art
- Superbia depressa in fornace babilonica (1687 Foggia / Capistrelli), oratorio
- La fornace di Nabuc di Nasor (1688 Pagano), oratorio
- Il convito di Baldassarro (Belshazzar's Feast / 1691 Albergati / Cintoli), oratorio
- Liber Tobiae, Judith, Oratio Manassae, Sapientia, et Ecclesiasticus Graecè et Latine (OT Apocrypha / 1691 Fabricius), book
- Le nozze di Tobia (1692 Viviani / Fineschi), oratorio
- Il viaggio di Tobia (1695 Casini), oratorio
- I fanciulli babilonesi (The Babylonian Children / 1696 Orlandini), oratorio
- Il ritorno di Tobia (1698 Badia / Del Negro), oratorio
- Daniele (Daniel / 1709 Rotondi / Grappelli), oratorio
- Susanna and the Elders (1713 Ricci), art
- Tobia (1720 Porsile / Zeno), oratorio
- Il ritorno di Tobia (1723 Lotti / Melani), oratorio
- The Accused Susanna and the Prophet Daniel (1726 Ricci), art
- Tobia il giovine (1727 Galuppi / Giupponi), oratorio
- Daniello (Daniel / 1731 Caldara / @1731 Zeno), oratorio
- Daniello (Daniel / 1731 Hasse / @1731 Zeno), oratorio
- Il cantico de' tre fanciulli (1734 Hasse / Pallavicini), oratorio
- Tobias and the Angel (1740 Giaquinto), art
- Il profeta Daniele (Daniel the Prophet / 1744 Bigaglia / Giupponi), oratorio
- Belshazzar (1745 / @1745 Haendel), London production, world premiere (oratorio)
- Belshazzar (1745 Haendel / Jennens), oratorio
- Susanna (1749 Haendel), oratorio
- Tobia (1749 Orlandini / Zeno), oratorio
- Daniel (1752 Werner), oratorio
- Il sogno di Nabucco (1755 Jommelli), oratorio
- Daniello (Daniel / 1767 Felici / @1731 Zeno), oratorio
- Colección de varias historias (1767-1768 Santos Alonso), novel
- Daniello (Daniel / 1772 Coccia / @1731 Zeno), oratorio
- Tres pueri hebraei in captivitate Babylonis (1774 Galuppi / Chiari), oratorio
- Tres pueri hebraei in camino ignis ardentis (1780 Bianchi), oratorio
- Daniele nel lago dei leoni (1781 Nicolini), oratorio
- Aurea statua a rege Nabucodonosor erecta; vel, Pueri Hebraei in fornace ardentis ignis (1783 Furlanetto), oratorio
- The Madness of Nebuchadnezzar (1793-1795 Blake), art
- I tre fanciulli ebrei liberati dalla fornace (The Three Jewish Children Rescued from the Furnace / 1798 Bellini / Russo), oratorio
- Ciro in Babilonia (Cyrus in Babylon / 1812 / @1812 Rossini), Ferrara production, world premiere (opera)
- Ciro in Babilonia (Cyrus in Babylon / 1812 Rossini / Aventi), opera
- Ciro in Babilonia (Cyrus in Babylon / 1813 / @1812 Rossini), Mantua production, world premiere (opera)
- Ciro in Babilonia (Cyrus in Babylon / 1817 / @1812 Rossini), Padua production (opera)
- Ciro in Babilonia (Cyrus in Babylon / 1820 Raimondi / Bordese), opera (music & libretto)
- I tre fanciulli nella fornace di Babilonia (1824 Bonfichi / Rasi), oratorio
- Ciro in Babilonia (Cyrus in Babylon / 1832 / @1812 Rossini), Perugia production (opera)
- Daniel the Prophet (1833 Horncastle), oratorio
- Belshazzar's Feast (1834 Griesbach), oratorio
- Il Daniello (1834 Terziani / Giuliani), oratorio
- Nabuchodonosor (Nebuchadnezzar / 1836 Anicet-Bourgeois, Cornu), play
- Nabuccodonosor (Nebuchadnezzar / 1838 Cortesi), ballet
- Balsazar (1840 Schumann), song
- Nabucco (1842 Verdi / Solera), opera
- Daniel (1852 Lake), oratorio
- Daniel (1853 Root/Bradbury), oratorio
- Belshazzar's Feast (1860 Root / Edmands), oratorio & libretto
- Tobias and the Angel (1863 Rosales), art
- Exiles in Babylon; or, Children of Light (1864 Tucker), children's novel
- Daniel (1866 Bristow / Hardenbrook), oratorio
- Daniel (1885 Bridge), oratorio
- The Three Holy Children (1885 Stanford), oratorio
- The Exile and the Restoration (1897 Davidson), book
- A History of the Jewish people during the Babylonian, Persian and Greek Periods (1899 Kent), book
- Tobit and the Babylonian Apocryphal Writings (1903 Sayce), book
- Belsazars gästabud (1906 Sibelius), theatre music
- Die Genealogie des Königs Jojachin und seiner Nachkommen (The Genealogy of King Jehoiachin and His Descendants / 1902 Rothstein), book
- Le festin de Balthazar (The Feast of Balthazar / 1910 Feuillade), short film
- Daniel (1912 Reuchael / Brody), oratorio
- Susanna and the Elders (1913 Stuck), art
- Daniel in the Lion's Den (1917 Fisher / McCarthy), oratorio
- The Court of Belshazzar (1918 Williams), novel
- Theatre Music to Roche's Belshazzar (1924 Achron), music
- Belsazar, das Ende Babylons (1924 Welten), novel
- Nebukadnezar, der König der Könige (1924 Welten), novel
- In the Palace of Amuhia (1926 Pickard), novel
- Belshazzar (1928 Haggard), novel
- Nabonidus and Belshazzar (1929 Dougherty), book
- Tobias and the Angel (1931 Bridie), play
- Daniel in the Lion's Den (1938 MacGimsey), oratorio
- I tre fanciulli nella fornace ardente (The Three Children in the Fiery Furnace / 1940 Maffeis / Palestra), opera
- Babylon (1946 Figuli), novel
- Nabucco (1949 Gui, Bechi / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Nabucco (1951 Previtali, Silveri / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1952 Kubelik / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1953 Boult / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Miracles of Faith (1953 Milhaud), oratorio
- Nabucco, German ed. (1955 Klobucar, Colombo / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Pravietis Daniels (1956 Kenins), oratorio
- The Exilic Age (1957 Whitley), book
- The Fiery Furnace (1958 Castelnuovo-Tedesco), oratorio
- Belshazzar's Feast (1958 Sargent / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1959 Walton / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Nabucco (1959 Bartoletti, Bastianini / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Nabucco (1960 Schippers, MacNeil / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Nabucco (1960 Singer, Winters / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Nabucco (1960 Vernizzi, Dondi / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Nabucco (1961 Bartoletti, Bastianini / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1961 Ormandy / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1961 Wagner / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Nabucco (1963 Rescigno, Protti / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Nabucco (1965 Gardelli, Gobbi / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- The Burning Fiery Furnace (1966 Britten / Plomer), opera (music & libretto)
- Nabucco (1966 Gavazzeni, Guelfi / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Exile and Restoration (1968 Ackroyd), book
- Nabucco, Bulgarian ed. (1968 Raichev, Popov / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Jews in Babylonia (1969 Reznikoff), poetry
- The Babylonian Captivity and Deutero-Isaiah (1970 Kaufmann), book
- Belshazzar's Feast (1972 Abravanel / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1972 Previn / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1973 Loughran / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Daniel in the Lions' Den (1973 Pinkham), oratorio
- It's Cool in the Furnace (1973 Red / Hawthorne), oratorio
- Sosanna és a vén (1976 Weinstock), novel
- Nabucco (1977 Muti, Nimsgern / Ronconi, Pizzi / 1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1977 Gibson / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1977 Solti / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Nabucco (1978 Muti, Manuguerra / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Nabucco (1979 Santi, Milnes / Ronse, Flédérick / 1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Nabucco (1981 Arena, Bruson / Giacchieri, Large / @1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Nabucco (1982 Sinopoli, Cappuccilli / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- The Writing on the Wall (1983 Garfield / Bragg), children' s novel
- The King in the Garden (1984 Garfield / Bragg), children' s novel
- Daniel and His Friends (1984 Matthews / Bishop), children's novel
- The Greatest Adventure: Daniel and the Lions' Den (1985 Patterson), animated TV short film
- Belshazzar's Feast (1985 Previn / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Nebuchadrezzar and Babylon (1985 Wiseman), book
- Daniel and the Lion's Den (1986 Benagh, Marks), novel
- Nabucco (1986 Muti, Bruson / De Simone, Large / @1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1988 Hickox / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1988 Shaw / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1989 Willcocks / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- A história de Tobias (1989 Rovisco), play
- Belshazzar's Feast (1990 Slatkin / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- The Story of Susanna (1990 Weinstock / Szasz), novel (English ed.)
- Nabucco (1991 Oren, Bruson / De Hana, Cavassilas / 1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Nabucco (1992 Guadagno, Cappuccilli / De Bosio, Casalino / @1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- I superstiti della deportazione sono là nella provincia (1993 Bianchi), book
- Belshazzar's Feast (1994 Davis A. / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1995 Litton / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- The Jewish Novel in the Ancient World (1995 Wills), book
- Nabucco (1996 Cillario, Summers / Kosky / 1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- On the Road with the Archangel (1997 Buechner), novel
- Nabucco (1997 Carignani, Bruson / Sparvoli, Licastro / @1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Belshazzar's Feast (1997 Rattle / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Nabucco (1998 Oren, Bruson / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Tobia e l'angelo (1998 Tamaro), novel
- Belshazzar's Feast (1999 Davis A. / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- The Madness of King Nebuchadnezzar (1999 Henze), book
2
- == == 2000s == == ==
- Nabucco (2000 Lessky, Donati / Werner / @1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Nabucco (2001 Attanasi, Kalmandi / @1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Belshazzar's Feast (2001 Daniel / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Nabucco (2001 Luisi, Nucci / Krämer, Reitzenstein / @1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Nabucco (2002 Levine, Pons / Napier, Large / 1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Nabucco (2004 Frizza, Gazale / Miller, Dorigo / @1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Nabucco (2004 Oren, Maestri / Panizza / @1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Belshazzar's Feast (2005 Davis C. / @1931 Walton), sound recording (oratorio)
- Nabucco (2007 Märzendorfer, Morosow / Herzl, Dolezal, Rossacher / 1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Nabucco, English ed. (2005 Parry, Opie / @1842 Verdi), sound recording (opera)
- Nabucco (2007 Oren, Nucci / Krief, Mancini / @1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Prince of Dreams (2008 Booth), novel
- Belshazzar (2008 Jacobs / @1745 Haendel), Aix-en-Provence production, video recording (oratorio)
- Daniel and the Lord of Lions (2008 Pinkney / Casilla), children's novel & art
- Nebuchadnezzar: the Head of Gold (2009 Chambers), novel
- Exile and Restoration Revisited (2009 Knoppers/Grabbe), edited volume
- Nabucco (2009 Mariotti, Nucci / Abbado, Mancini @1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- == == 2010s == == ==
- Belshazzar (2013 Christie / @1745 Haendel), sound recording (oratorio)
- Nabucco (2013 Luisotti, Domingo / Abbado / @1842 Verdi), video recording (opera)
- Sworn Enemies: The Divine Oath, the Book of Ezekiel, and the Polemics of Exile (2013 Strine), book
- The Book of Daniel (2013 Zielinski), feature film
- Daniel (2015 Montez), oratorio
Media in category "Babylonian Exile (subject)"
The following 4 files are in this category, out of 4 total.
- 1916 Griffith (film).jpg 403 × 599; 80 KB
- 1931 * Walton (oratorio).jpg 340 × 499; 25 KB
- 1970 * Ackroyd.jpg 375 × 499; 24 KB
- 2013 Downey (TV miniseries).jpg 349 × 500; 67 KB